Why might my surgeon suggest spinal fusion surgery?
Fusion is often prescribed when spinal degeneration and/or instability prevents normal function or is causing back pain that has impacted your lifestyle and has not improved with conservative treatment. Additionally, fusion is often performed when an acute condition requires emergency intervention to prevent further injury
What is spinal fusion surgery?
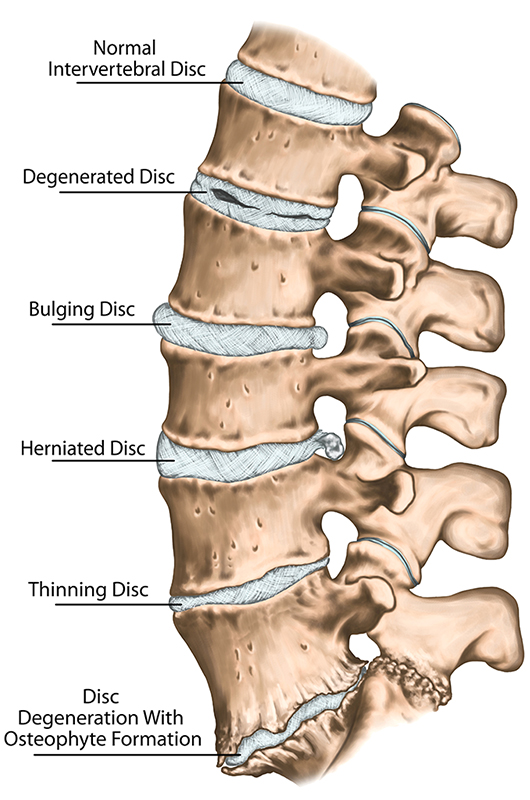
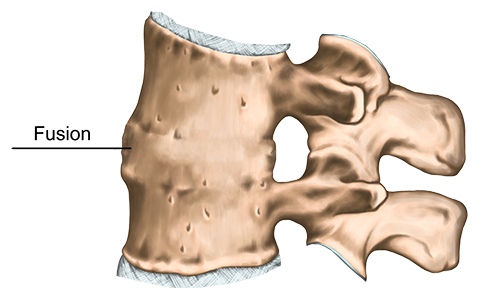
Fusion surgery provides stability to unstable spinal segments in the neck (cervical) or lower back (lumbar) by permanently joining (fusing) two or more adjacent vertebrae in the spine.
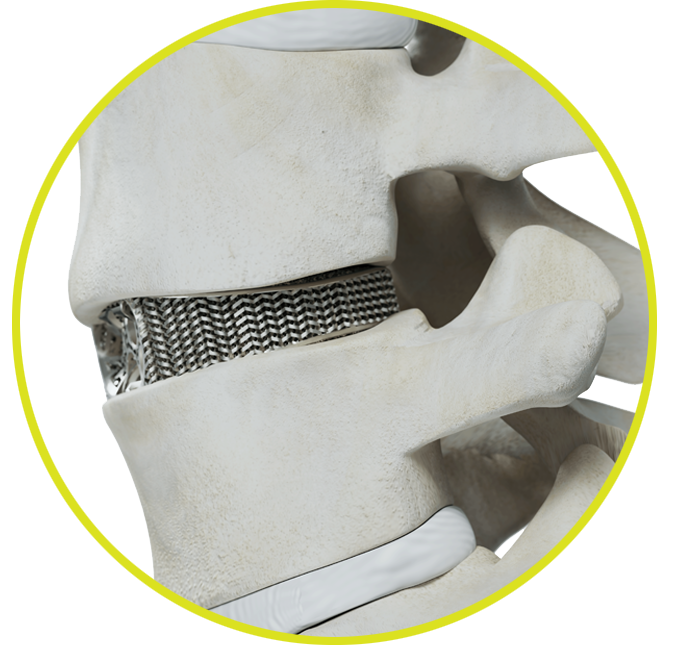
What is the purpose of an interbody fusion device?
The purpose of an interbody fusion device is to stabilize adjacent vertebral bodies and hold them in proper position to help provide an optimal environment for healing while fusion (bone growth) occurs. They also serve to restore proper disc height in situations where height has been lost due to degeneration.
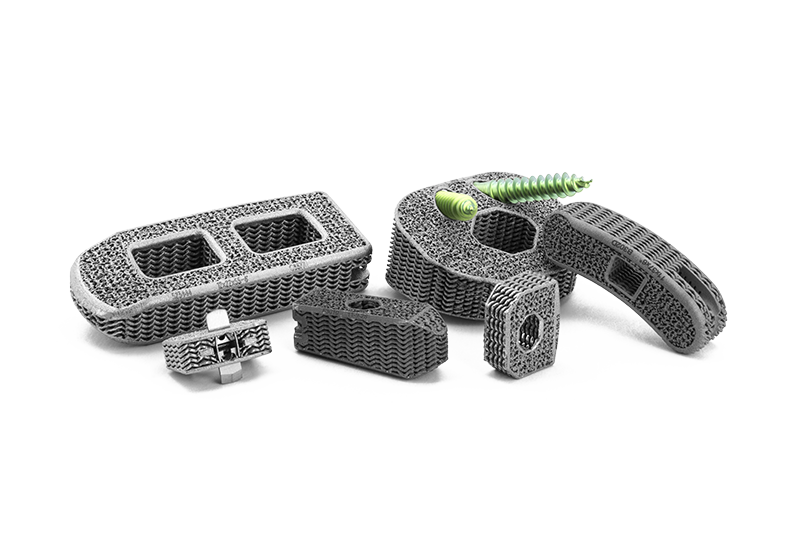
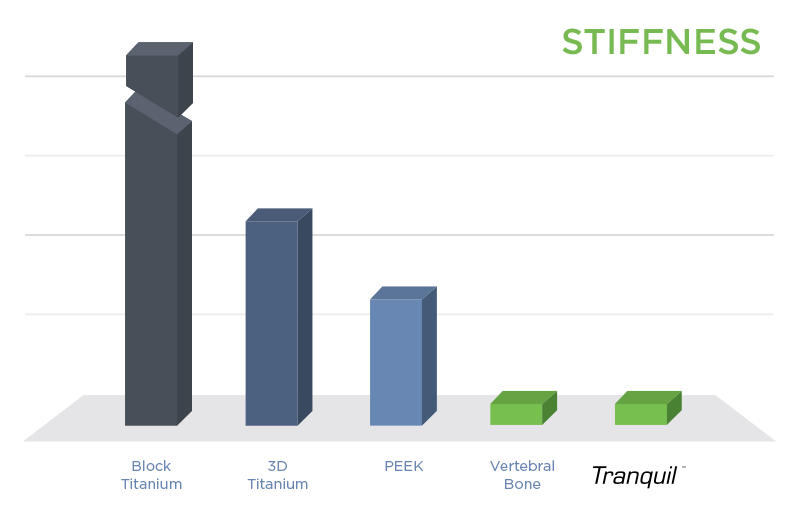
How are Tranquil™ interbody fusion devices uniquely designed to promote successful spinal fusion?
Tranquil™ interbody fusion devices are the only available implants to match the stiffness of spinal bone.1 Matched stiffness places the correct amount of load on the vertebrae to promote rapid stability, fusion, and healing.2 Other devices are too stiff, which shield the fusion mass from receiving enough load and hinder development of healthy bone. Overly stiff implants also concentrate loading on portions of the vertebral endplate that can lead to collapsing of the device into the vertebrae (subsidence).
Further, Tranquil™ possesses a unique surface architecture at the cellular level that promotes the production of bone growth factors necessary for bone production and fusion.3 This process, in addition to bone-matched stiffness, encourages rapid boney attachment, integration with the vertebral endplate, and stability.
Tranquil™ incorporates novel material properties, technology, and engineering to create an environment that is favorable for boney fusion.
Citations:
- Data on file: NX19-103
- Lane, J. M., et al. “Materials in fracture fixation.” (2011): 219-235.
- Data on file: NX19-104.